The electronic control system is part of the EFI system that controls the amount of fuel injection and ignition time according to the working conditions of the engine.
Utilization as a controller electronic injection system and ignition time enables the accuracy of the fuel mixture and ignition time most optimal, so the economical fuel consumption, low exhaust emissions and optimum engine performance.
The
electronic control system can be grouped into three, namely:
1.
The sensor is used to detect the condition of the vehicle as input to the ECU.
2. Electronic Control Unit (ECU) functions to process input from sensors to
control the actuator.
3. Actuators
are part controlled by the ECU to take action in accordance with the
signal from the ECU.
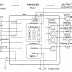
Chart electronic control system can be described as following:
1. SENSOR
There are many sensors that are used by EFI engine. Here are the types of sensors and sensor functions and function is as follows:
a.Water Flow Meter
Air flow meter serves to measure the amount of air into the cylinder as the basis for ECU to determine the amount of the injection.
c. Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
Throttle position sensor (TPS) is mounted on the throttle body. TPS function is to detect the position of the gas valve openings (Throttle valve).
d. Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS)
Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS) is a sensor used to detect the temperature of air entering the cylinder.
e. Water Temperature Sensor (ECTS)
Water Temperature Sensor (WTS) or Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECTS) is used to detect the engine temperature through the engine cooling water. WTS installed near the home thermostat or cooling channels, end of sensors contact with the cooling water.
f. oxygen Sensor
Oxygen sensors are used to detect the exhaust gas, to determine if the fuel air mixture (AFR) is too rich, or too poor, or right. Based on the feedback of oxygen sensor if the mixture is too rich, the ECU will reducing injection and when the mixture is poor then the ECU will add to the fuel injectors. Oxygen sensors used in vehicles using catalytic converters.
h. Vehicle Speed Sensor
Vehicle Speed Sensor is used to detect the speed of the vehicle. with the speed sensor causes the ECU obtain more complete information about the condition of the vehicle. With the combination of information from TPS, MAP sensor, NE signals, and speed sensors, the ECU can determine if the current vehicle acceleration, deceleration, idle or under heavy loading.
i. knock Sensor
Knock sensor function detects vibration cylinder block due to knocking . Knock sensor installed on the cylinder block. Knock sensor consists of a piezoelectric element and a diaphragm.
a.Water Flow Meter
Air flow meter serves to measure the amount of air into the cylinder as the basis for ECU to determine the amount of the injection.
b. Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP Sensor)
MAP sensor is used to measure the amount of air into the cylinder by the air pressure in the intake manifold. MAP sensor used on EFI-D. These sensors are often called Intake Manifold Pressure sensor (PIM) or Vacuum sensor.
Data from the MAP sensor as a basis for determining the amount of injection and ignition time. The main advantages MAP sensor compared air flow meter to measure the amount of air is less mechanical parts, are not influenced by leaks in the manifold and outside air pressure changes.
Throttle position sensor (TPS) is mounted on the throttle body. TPS function is to detect the position of the gas valve openings (Throttle valve).
Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS) is a sensor used to detect the temperature of air entering the cylinder.
Intake air temperature sensor is a thermistor, a resistor whose value is changed according to changes in temperature. type thermistor is the Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC), the higher the temperature the lower the value of the resistor. IATS installed near the house air filter, or conduit between the air filter with throttle body.
Water Temperature Sensor (WTS) or Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECTS) is used to detect the engine temperature through the engine cooling water. WTS installed near the home thermostat or cooling channels, end of sensors contact with the cooling water.
f. oxygen Sensor
Oxygen sensors are used to detect the exhaust gas, to determine if the fuel air mixture (AFR) is too rich, or too poor, or right. Based on the feedback of oxygen sensor if the mixture is too rich, the ECU will reducing injection and when the mixture is poor then the ECU will add to the fuel injectors. Oxygen sensors used in vehicles using catalytic converters.
g. variable Resistors
Variable resistor is a component that is used on vehicles not equipped with catalytic conventer, instead of the oxygen sensor. On vehicles that use oxygen sensor fuel mixture adjustment can be performed automatically according to the signal from the oxygen sensor. For vehicles that do not use oxygen sensor fuel mixture adjustment is done by adjusting the variable resistor. This component is also often called CO adjuster. When setting the mixture should use CO tester. Do not try adjust the fuel mixture when not using CO tester, because the results of adjustment can be greatly distorted.
Inspection the variable resistor can be done with the approach of voltage, voltage 0 - 5V at terminal VAF - E2, can also measure the value of the resistor between terminal VAF-E2 with 5Ω.
Vehicle Speed Sensor is used to detect the speed of the vehicle. with the speed sensor causes the ECU obtain more complete information about the condition of the vehicle. With the combination of information from TPS, MAP sensor, NE signals, and speed sensors, the ECU can determine if the current vehicle acceleration, deceleration, idle or under heavy loading.
i. knock Sensor
Knock sensor function detects vibration cylinder block due to knocking . Knock sensor installed on the cylinder block. Knock sensor consists of a piezoelectric element and a diaphragm.
j. Signal distributor
Distributor signal is generated signal distributor as an input to the ECU to determine engine rotation and crank angle. Based on the input signal distributor to the ECU, ECU determines ignition timing and injection timing. There are two models of signal distributors, namely: signal generator models and models of photo diode.
k. Starter Signal
Starter signal functions as a signal to the ECU that the engine is in the starter. Based on these inputs the ECU will increase the amount of fuel injection so that the mixture richer. As such engine more easily turned on.
l. Air Conditioning (AC) Signal
AC signal gives information to the ECU that the AC was turned on, with the input, the ECU will activate Vacuum Switch Valve (VSV).
When VSV becomes ON so that there is a by-pass air into the cylinders for more. Increased air entering the cylinders is detected by the MAP sensor, and sends a signal to the ECU so the ECU increase the amount of fuel. Increasing the amaunt of fuel injection causes increased idle rotation (idle-up).
2. ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (ECU)
ECU is a microcomputer that functions to control the electrical system of the vehicle. ECU is often also called Electronic Control Module (ECM) and Electronic Management System (EMS) because part of the governing system electronic.
he sensors are grouped into two, namely:
a. Sensors with analog signal
Signal with continuous change. For example: Intake air temperature sensor, air flow meter, throttle position sensor, MAP sensor, water temperature sensor, knock sensor and signal NE. Signal from the sensor is converted by a series of A / D converter into a digital signal.
b. Sensors with digital signal
Digital signal is a signal with two conditions, namely: 0 or 1, ON OFF,
or high-low. For example: starter signal, the ECU will get a signal "1" when the engine-started and got a signal "0" when the engine is switched off or already run. The sensors provide input to the microcomputer. Based on these inputs microcomputer perform the counting process and the appropriate adjustments to existing programs to determine the output signal to the actuator.
Microcomputer consists of:
1. CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Perform the counting process input data and storing that data in accordance with program stored on ROM.
2. ROM (Read Only Memory)
Store programs and data necessary for the counting process. Although the power OFF program content is retained, but the contents of the program can not be rewritten.
3. RAM (Random Access Memory)
Store data temporarily while the vehicle is in operation, when the power OFF then the data will be erased.
3. ACTUACTOR
Actuactors is part controlled by the ECU to take action in accordance with the signal from the ECU. Igniter is controlled by the ECU to determine (dwell angle) and the time of ignition, the injector is controlled by the ECU when the injection, determine the duration and pattern of fuel injection, vacuum switch valve (VSV) is controlled by the ECU as idle up or idle speed control (ISC). The fuel pump works or ON only when the engine started and when the engine is on, when the contact OFF or contact ON but the machine is OFF then the relay will be OFF. The pump works only when the pump relay function. The function of the pump relay is controlled by the ignition key when the starter, switch on the air flow meter and the ECU. Engine check indicator is controlled by the ECU to provide the code with the blinking (lights ON / OFF) according to the disturbance.
a. Igniter
Igniter is a main component of the ignition system. Igniter functions to connect and disconnect power to the primary coil to the ignition coil generates a high voltage induced in the secondary coil, high voltage induction subsequently channeled to the spark plugs and then to spark plugs produce fire to burn the fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
b. injector
The injector is one of the main actuactor the EFI system. Injector serves to inject fuel toward the suction valve, the fuel out of the injector in the form of mist. The amount of fuel injected depends on the fuel pressure, the hole injector and injector duration open.
The opening of the electromagnetic injector performed, by an electric discharge in coil injector. When electricity flows into the injector coil, the coil core becomes a magnet and the magnet pulls injector against the valve spring. when the injector needle is is pulled, the hole injectors open and inject fuel, when the power stopped then magnetic the resulting coil is lost, due to the spring force pushed, the injector needle closes the hole.
---------



















This is really a nice post and worked for me. thanks
ReplyDelete